What Is Automobile Engineering?
Automobile engineering is a specialized field of study and practice that deals with the intricate processes involved in designing, developing, manufacturing, and maintaining vehicles. This branch of engineering combines elements of mechanical, electrical, and electronic engineering, along with aspects of software and safety engineering. Automobile engineers play a crucial role in shaping the technology and innovation behind cars, motorcycles, trucks, and other types of vehicles. They work on diverse aspects, including the design and optimization of vehicle systems, engines, transmissions, suspension systems, and more. The field continually evolves to address challenges related to fuel efficiency, environmental impact, safety features, and the integration of cutting-edge technologies, such as electric and autonomous vehicles.
Let’s see the car from various angles in order to know what kind of machine the car is.
(1) Definition of automobile.
An automobile is a vehicle that typically carries a prime mover (engine or motor), has a steering device (device for changing the direction), and uses a wheel with a rubber tire to drive it and freely travel on the road.
It consists of various interconnected mechanical and electrical components that work together to facilitate movement. Let’s delve into the key aspects that define a car machine:
Prime Mover (Engine): At the heart of every car is its engine, which serves as the prime mover. Most cars utilize either an internal combustion engine (running on gasoline, diesel, or alternative fuels) or an electric motor. The engine generates the power required to drive the vehicle.

Steering System: Cars are equipped with a steering system that allows the driver to control the direction of the vehicle. Common steering systems include rack-and-pinion, recirculating ball, and electric power steering, each contributing to the car’s maneuverability.
Wheels and Tires: The wheels, typically made of metal, support the vehicle’s weight and provide a platform for the tires. Rubber tires, usually filled with air, offer traction and grip on the road, contributing to the car’s stability and handling.
Transmission System: The transmission, whether manual or automatic, manages the power generated by the engine and transmits it to the wheels. It allows the driver to control the speed and direction of the car efficiently.
Suspension System: The suspension system comprises components like springs, shock absorbers, and struts. It ensures a smooth ride by absorbing shocks and vibrations, while also maintaining tire contact with the road for better handling.
Braking System: To control the car’s speed and bring it to a stop, a braking system is essential. Common types include disc brakes and drum brakes, which convert kinetic energy into heat to slow down and stop the vehicle.
Fuel System (Internal Combustion Engines): In cars with internal combustion engines, a fuel system is crucial for delivering the appropriate fuel-air mixture to the engine cylinders. This system includes components like fuel injectors, carburetors, and fuel pumps.
Electrical System: Modern cars incorporate an intricate electrical system, consisting of a battery, alternator, starter motor, and various sensors. This system powers the lights, entertainment systems, ignition, and electronic components crucial for the car’s operation.
Exhaust System: The exhaust system expels the byproducts of the combustion process, such as gases and pollutants, safely away from the vehicle. It typically includes a catalytic converter to reduce emissions.
Cooling System: Engines generate a significant amount of heat, and a cooling system is vital to regulate temperature. Radiators, coolant, and a water pump work together to dissipate excess heat and prevent engine overheating.
Body and Frame: The car’s body and frame provide structural integrity and house the passenger compartment. The design and materials used in the body contribute to safety, aerodynamics, and overall aesthetics.
(2) Classification of cars
Cars are categorized according to the type of engine installed, the position of the engine, the driving method, and the use purpose.
① Classification by type of engine
◆ Gasoline engine car

It is a car equipped with an engine that uses gasoline as a fuel.
Gasoline engines are mounted in many passenger cars because of their small size, lightweight, high output, and low vibration and noise.
◆ Diesel engine car

It is a car equipped with an engine that uses diesel as a fuel.
Diesel engines are economical because of low fuel costs and good fuel economy.
However, it is inferior to gasoline engines in terms of vibration, noise, acceleration, etc. It is mainly mounted on trucks and RV cars.
◆ LPG engine car
It is a car equipped with an engine that changed part of the gasoline engine so that LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) can be used for fuel.
Like the gasoline engine, the LPG engine is lightweight, low vibration, and low noise.
But power is inferior to gasoline engines. LPG is cheaper and more economical than gasoline.
Classification by engine mounting position, driving method
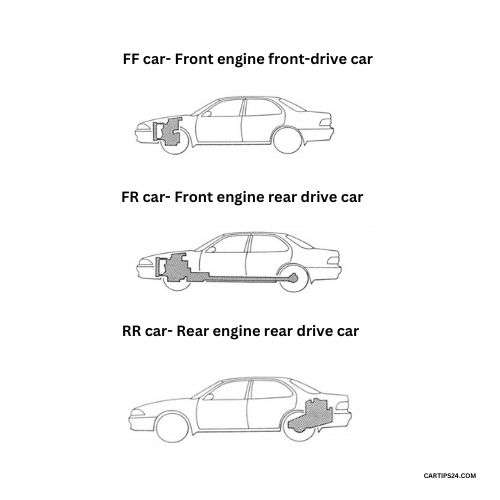
◆ FR car – Front engine rear drive car
It is a method of driving the rear wheels by mounting the engine on the front of the vehicle. Because the steering wheel and the driving wheel are separate, the weight distribution is good, and the operability and stability are excellent. It is widely adopted for large passenger cars and trucks.
◆ FF car …… Front engine front-drive car
It is a method of driving the front wheels by mounting the engine on the front part of the vehicle. Because there is no device to transmit power to the rear wheels, it has the characteristics of a compact, lightweight power transmission device and a big interior space. It is widely adopted for compact passenger cars.
◆ RR car …… Rear engine rear drive car
It is a method of driving the rear wheels by mounting the engine behind the rear axle. Like the FF car, it is characterized by the lightness and large size of the interior, but it has drawbacks (disadvantage) that it is difficult to secure the trunk space. It is used for some sports cars.
◆ MR car …… Mid-ship engine rear drive car
It is a method of driving the rear wheels by installing the engine in front of the rear axle. Weight distribution is ideal and high running performance can be demonstrated. However, the interior is small, and it has a weakness against vibrations and noise. It is adopted for some sports-type cars.
0-5
◆ 4WD car …… 4 wheel drive car
Transmit the power to the front and rear wheels, it is a method to drive at the same time. It has good running performance on bad roads and snowy roads and is characterized by its high running performance. It is used for passenger cars, trucks, and RV vehicles.
Classification by purpose
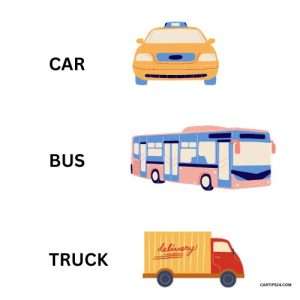
◆ Passenger Car
It refers to a car intended to transport a small number of people (generally 10 people or less).
◆ Bus
It refers to a car intended to transport a large number of people (generally one or more people).
◆ Track
It is a car aimed at transporting luggage.
◆ Other
There are motorcycles, trailer trucks, and special-purpose vehicles (such as patrol cars, and fire engines).



