In the realm of automotive safety, one crucial component stands out – the car brake system. Without a reliable braking mechanism, our vehicles would be hazardous to operate. Let’s delve into the basics of car brake systems, exploring their types, components, and functionalities.
Role of brake- How do brakes stop a car?
An automobile can run by rotating a tire that is in contact with the ground. And the faster the tire rotates the faster the car can run. On the contrary, if the tire does not rotate, no matter how much the engine rotates it cannot move the car.
The brake slows down or stops the rotation of this tire, slowing the speed of the car and stopping the car. It is also the role of the brake to keep stopped cars stopped.
The brake of an automobile is roughly divided into two by function, depending on its role.
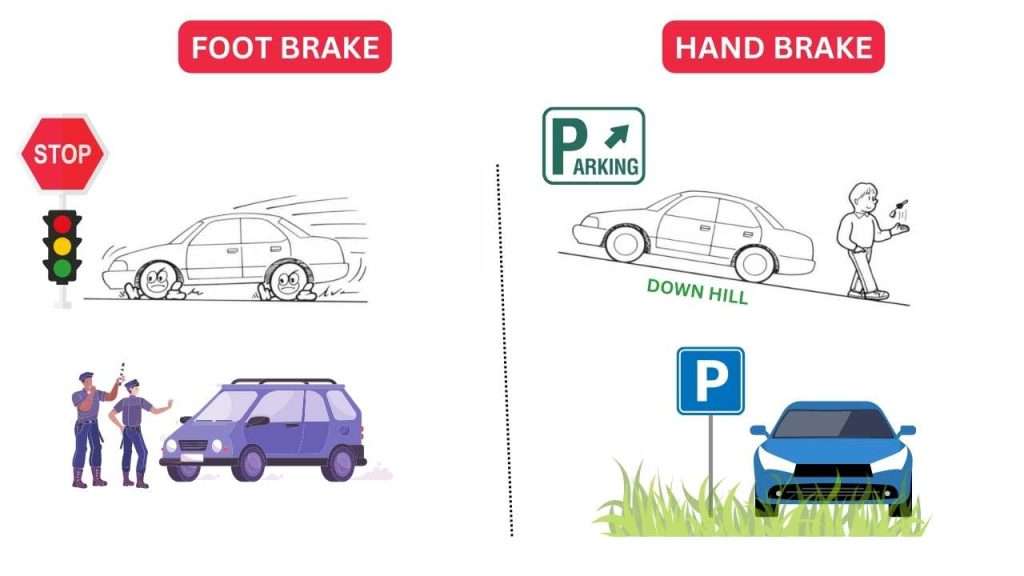
Foot brake
Foot brake Reduce the car speed and stop the car. Foot brake Speed down or stop the rotation of the tire to reduce the speed of the car and also help to stop the car.
In automobiles, the term “foot brake” typically refers to the primary braking system controlled by the driver’s foot. This system is more formally known as the “service brake” and is responsible for slowing down or stopping the vehicle during normal driving conditions. The foot brake is a crucial component of a car’s overall braking system and plays a key role in ensuring the safety of both the occupants and other road users.
How does a foot brake work?
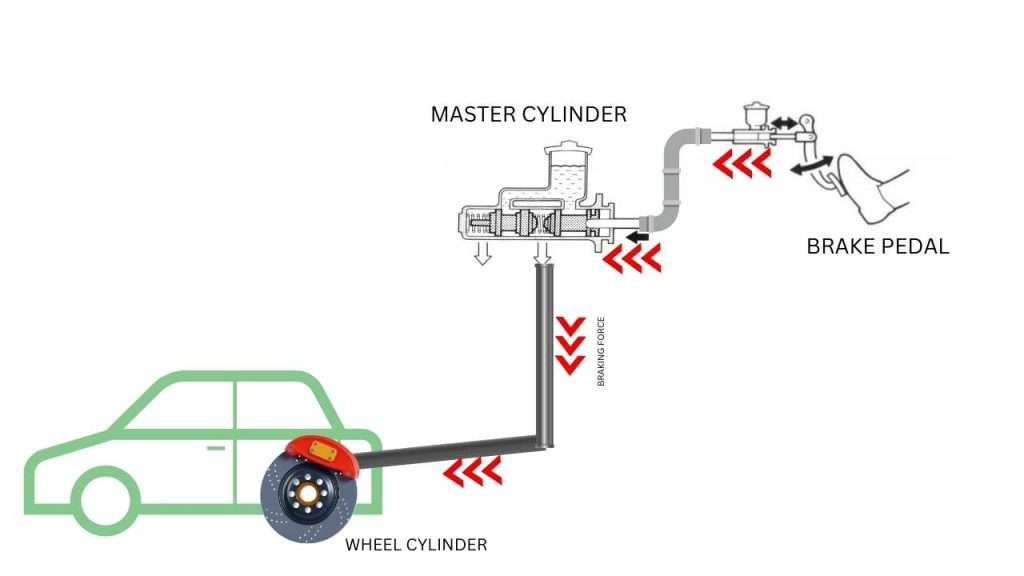
Brake Pedal- The foot brake is operated using the brake pedal located in the driver’s compartment. When the driver presses the brake pedal with their foot, it initiates a series of mechanical or hydraulic actions within the braking system.
Foot brake type – Hydraulic or Mechanical Action: In modern cars, the foot brake is commonly part of a hydraulic braking system. When the brake pedal is depressed, hydraulic fluid is pressurized, transmitting force to the brake components. In older vehicles, especially those with drum brakes, a mechanical linkage may be used instead of hydraulic pressure.
Foot Brake Components: The foot brake system includes various components, such as brake calipers (for disc brakes) or wheel cylinders (for drum brakes), brake pads or shoes, and brake rotors or drums. When the brake pedal is pressed, these components work together to create friction and slow down the rotation of the wheels.
Parking brake
In automobiles, a parking brake, also commonly known as a handbrake or emergency brake, is a secondary braking system designed to secure a parked vehicle in place. Unlike the primary foot-operated brake system that slows down or stops the vehicle while it is in motion, the parking brake is specifically intended for use when the vehicle is stationary. The parking brake serves two main purposes:
Preventing Movement: The primary function of the parking brake is to prevent the vehicle from rolling or moving when parked. It adds an extra layer of safety, especially on inclines or uneven surfaces, where relying solely on the transmission’s “park” position may not be sufficient.
Emergency Use: As the alternative name suggests, the parking brake can also be used in emergency situations. For example, if the primary brake system fails while driving, engaging the parking brake can help bring the vehicle to a stop.
Most parking brakes are manually operated and can be engaged by pulling a lever or pressing a button in the cabin.
How to Reduce the car speed and stop the car.
Let’s see the braking flow when the driver finds the danger until the car stops.
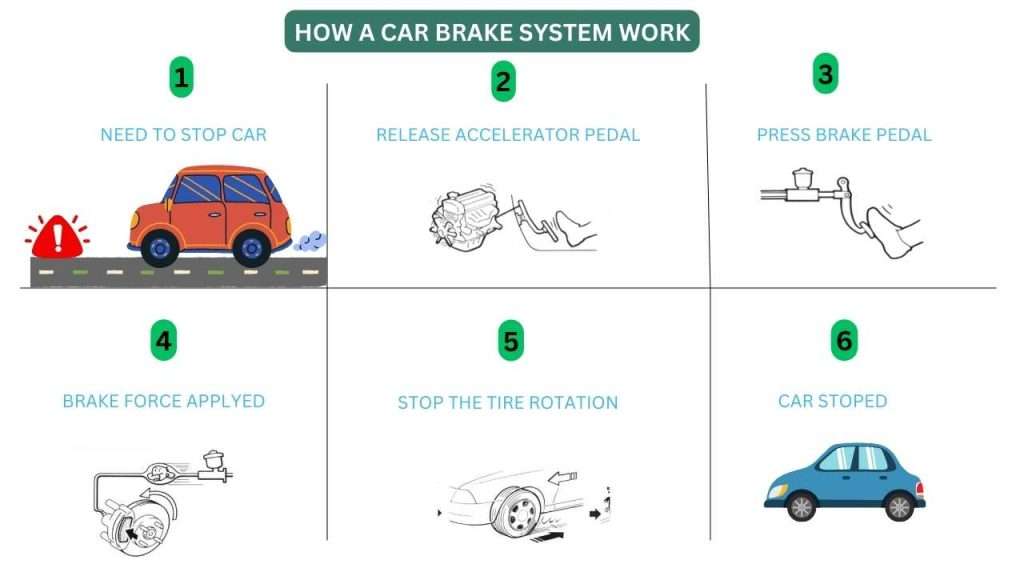
◆ when a driver holds down the brake pedal after finding the danger before the brake starts to work.
1-Driver Finds the danger and wants to stop the car.
2- The driver releases the accelerator pedal.
When stepping on the accelerator pedal, the engine generates a large force, and the engine turns the tire strongly.
When the accelerator pedal is returned, the force generated from the engine decreases, and it tries to go down to the idle rotation speed. Therefore, turning the engine in conjunction with the rotation of the tire will gradually slow down the rotation of the tire.
What is engine brake
While driving, when you return the accelerator pedal, the car slowly slows down. This is because the brake action by the engine works. This is called an engine brake.
3-driver Step on the brake pedal.
Why does the brake work if we step on the brake pedal?
When we step on the brake pedal, its force is transmitted to the master cylinder and pushes the piston. The piston pushes the fluid called brake fluid and transmits pressure (hydraulic pressure) to the brake body (brake calipers and wheel cylinders).
If the brake fluid piping breaks and the brake fluid leaks, the brake will not work. Therefore, the brake hydraulic pressure is divided into two systems and it is a mechanism that can generate hydraulic pressure.
Human reaction time and the time it takes for the brake to operate. This time is nearly constant, and the distance traveled during this time increases as the speed of the car increases.
◆ When a driver presses the brake pedal to stop the car and after the brake starts working.
1-Transmit force
The hydraulic pressure of the two systems sent from the master cylinder is transmitted to each wheel cylinder, but the layout of the brake piping differs between the FR car and the FF car.
FR cars are divided into front wheels and rear wheels, however, in FF cars piping is crossed. Because FF cars are heavier on the front wheels, the braking power of the front wheels is higher than the rear wheels. Therefore, in the same piping as the FR car, when the brake system for the front wheel breaks down since the braking force becomes weak, the piping is made to intersect like the right front wheel and the left rear wheel, the left front wheel and the right rear wheel, and one line In case of failure, we are able to ensure some degree of braking power by the remaining one system.
During running the car, the position of the wheel cylinder will change depending on the condition of the road surface and the movement of the steering wheel. In order to respond to changes in the position, a rubber brake hose is used instead of a metallic brake tube at the part where the piping moves. As the brake hose deteriorates over time, periodic replacement is necessary.
2-Stop the rotation of the tire
Pinch with a finger to stop the spinning top toy, you can feel the heat on the fingertips. This is because the heat was generated by friction between the pressed fingers and the shaft of the spinning top toy.
So why did the Top toy stop?
Spinning tops are spinning by rotating energy. By pinching the finger, this rotational energy was converted into thermal energy, the spinning top toy lost the rotational energy and stopped. Likewise, the brake of a car changes the rotation energy of the tire to thermal energy and stops the tire. When stopping the tire, a large amount of heat is generated, so it is important to take measures to dissipate heat for the brakes of automobiles. The brake body has roughly divided disc brake and drum brake.
3-The car stops
The car runs slow or stops the speed by slowing or stopping the rotation of the tires with a brake device. At that time, what kind of power is working on the car? Even if driving power from the engine is separated by stepping on the clutch while driving, the car will run for a while as it is. This is because the power to keep running to the car(Law of inertia)is working. To stop a running car is to generate a force between the road and the tire, that tries to stop it in the opposite direction to this driving force.
The braking distance varies with the balance between the force to keep running and the force to stop. Therefore, when you are running at high speed or running on a slippery road such as a snowy road, the braking distance will be long.
It gradually becomes a braking force and it is time until the car stops. The distance traveled during this time will vary greatly depending on the speed of the car, the condition of the road surface, and the state of the brake device.
The time from finding the danger until the car stops is the total time of these two times. Therefore, in order for the car to stop safely, it is important for the driver to operate at a speed according to the condition of the road surface and to keep the brake equipment in good condition at all times.
Types of Car Brake Systems

Hydraulic and mechanical brake systems are the two major categories. Hydraulic systems utilize brake fluid to transfer force, offering precise control. In contrast, mechanical systems employ cables and levers, often found in older vehicles.
When it comes to braking systems, two primary types dominate the automotive landscape: disc brakes and drum brakes. Disc brakes offer superior performance and heat dissipation, while drum brakes are more cost-effective and commonly found in rear-wheel systems.
Disc brake
The disc brake pushes the piston with the hydraulic pressure transmitted from the master cylinder via the brake tube and the brake hose and clamps the disc rotor which is rotating with the tire from both sides with the disc pad and stops the rotation of the tire.
Therefore, since the disc rotor and the disc pad chafe against each other, heat is generated during this time. However, since the disc rotor and brake body are exposed, frictional heat generated can be easily released.
Also, as the disk rotor and disk pad rub against each other, the disk pad gradually wears. However, even if the disc pad wears, the piston moves accordingly, so the momentum of the brake pedal does not change and the feeling of depressing the brake pedal does not change.
Furthermore, when the disc pad wears out and the remaining amount becomes low, the pad wear indicator comes into contact with the disc rotor, and a sound is generated to inform the driver
Drum brake
In the drum brake, there are brake shoes inside the brake drum, and by pressing these against the brake drum, the rotation of the tire is stopped. At this time, the brake shoes are stuck into the rotating brake drum, increasing the frictional force. Therefore, compared to the disc brake, strong braking force is obtained even if you press the brake pedal lightly.
However, since the brake shoes are surrounded by the brake drum, it is difficult to escape the generated heat and it can be said to be a weak brake against the heat. Also, if the brake shoe wears out and the clearance between the brake drum and the brake shoe expands, the movement amount of the brake shoe increases, and the brake pedal stepping distance increases, so it is necessary to periodically adjust the clearance. Therefore, in passenger car rear brakes, etc., a device that automatically adjusts the gap is installed.
Parking brake- How to Keep the car stop
The parking brake is used to keep a stopped car without stepping on the brake pedal.
Compared with the braking force to stop the running car, the braking force required for stopping the car is relatively small. So in a car, the parking brake is applied only to the rear wheels.
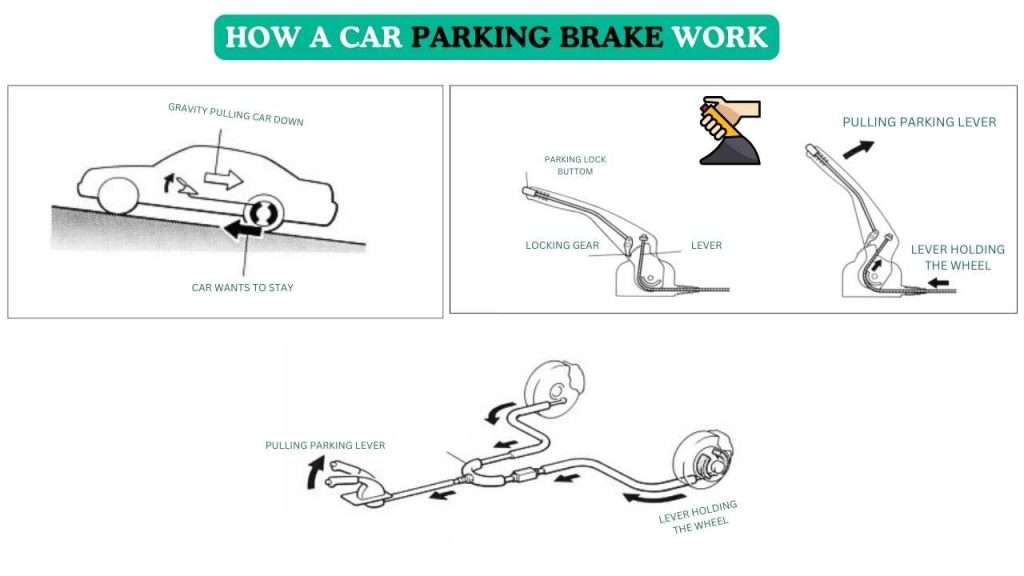
How parking brake works
1 – Pull the parking brake lever
The parking brake lever and brake device are connected by cables. When pulling the parking brake lever, the cable is pulled and the brake device is activated.
The parking brake lever has a lock mechanism so that it can be fixed in the pulled state.
Parking brake lever assembly
The parking brake lever assembly is a mechanical or electronic mechanism designed to engage and disengage the parking brake. The parking brake, also known as the handbrake or emergency brake, is a secondary braking system in a vehicle that is independent of the primary foot-operated brake system. The parking brake lever assembly typically consists of several components,
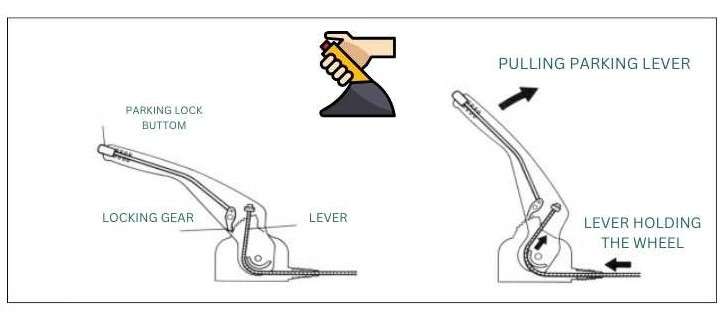
Lever: The physical handle or lever that the driver pulls or engages to activate the parking brake.
Cable or linkage: The mechanism that connects the parking brake lever to the rear brakes. When the lever is engaged, the cable or linkage transmits the force to engage the brakes.
Release button or lever: A feature that allows the driver to disengage the parking brake when pulling up the lever.
In many vehicles, the parking brake lever assembly is located between the front seats, either on the center console or directly on the floor. However, in some cars, especially those with electronic parking brake systems, the parking brake may be engaged or disengaged using a button or switch rather than a physical lever.
The parking brake serves various purposes, such as preventing the vehicle from rolling when parked on an incline, ensuring stability during maintenance or repairs, and providing an additional safety measure in emergency situations. The parking brake lever assembly is a crucial part of this system, allowing the driver to control and apply the parking brake manually.
2-Transmit brake power
One cable connected to the parking brake lever is divided into two through an equalizer from the middle to transmit the force to the rear wheel.
The equalizer applies equal force to the rear wheels evenly.
Type of parking brake
There are the following types of parking brakes.
Drum parking brake
Widely uses this type of car-adopted drum brake as a rear foot brake. Fix the tire using the same brake shoe as the foot brake.
The parking brake lever is attached to the rear brake shoe. By pulling the lever with the cable, the shoe strut is pushed to the left of the figure, so the left brake shoe is pressed against the brake drum. At the same time, using the shoe strut as a fulcrum, the brake shoes on the right side of the figure are pressed against the brake drum, so the brake works on the brake shoes on both sides.
Drum in disc type Parking brake
The large-sized passenger car uses this type. The foot brake of the rear wheels uses the disc brake, and the drum brake is used only for the parking brake. Adopted the drum-type parking brake in the center of the brake disc. Operation is the same as drum type.
Disc parking brake
Small passenger car uses this type of adopted disc brake as a rear foot brake. Fix the tire using the foot brake body.
Center-type parking brake
It incorporates a drum-type parking brake between the transmission and the propeller shaft. It is mainly adopted for buses and trucks. Since this type increases the braking force by being decelerated by the differential, even one can exhibit sufficient braking power.